What is the logical structure of the site and why is it needed
Author - Constantin Nacul
The foundation of the site is a properly created structure. However, there is no answer to the question of what it should be. It is only clear that for each project it must be selected strictly individually. There are also certain requirements of search engines that must be followed in any case. We'll talk about this.
What is the logical structure of the site
The logical structure of a site is a collection of all pages on a site, arranged according to a hierarchy. That is, the relationship of pages in which their belonging to sections, categories, subcategories and other types of pages (product cards, tags, filters, etc.) can be traced.
The structure of the site should be built in such a way as to make it easy for users to move from general topics to the specific information they came for. The convenience of the user, the time he will spend on your site, the targeted actions that he will perform depend on this. A confusing navigation system and over-structuring of content will not lead to anything good.
The importance of the correct site structure for search engines
Each search engine has its own structure requirements. I will describe the most basic of them.
Google site structure guidelines
1. Use a logical hierarchy. The user should be able to easily get to any page of your site. To do this, use the navigation bars, the so-called "breadcrumb". They will help the user find the right section and not get lost on the site. They look like this:
2. Use text, not banner (in the form of an image) links. This will give search robots the opportunity to more clearly assess the relevance of the link, that is, it will make it easier to crawl and analyze the content of your site pages.
3. For visitors, create a navigation page (HTML sitemap) and a Sitemap.xml file, in which specify the target URLs and the dates of the last changes, so that Googlebot can quickly find new and changed pages in your structure.
4. Create informative 404 pages. On the page, place links to the main page and popular sections of the site so that when going to a non-existent page, the user does not leave your site, but continues to search for the necessary information.
5. Use Human Understandable Page Addresses (NCPs) instead of identifiers. They are more understandable for the visitor, easier to remember and show which page the user is on.
For example, instead of https://site.com/index.php?cat=10&subcat=2&id=41, use https://site.com/product/phone/samsung/.
6. Create a simple directory structure so that it's easy to navigate the site, and the URL of the page reflects its content.
7. Use different URLs for different documents. There should be only one unique address per site.
Read more about Google recommendations in help.
Recommendations from Yandex
1. Keep a clear page hierarchy. Each document should have its own section.
2. Use a sitemap. Create a Sitemap file and upload it to Yandex.Webmaster or provide a link to the file in Robots.txt. The search robot will index and analyze the necessary documents faster.
3. Limit the indexing of service information using the Robots.txt file so as not to waste resources on pages that are unnecessary for the user.
4. Use unique page URLs. Each page should be accessible from only one address.
Make text links to other sections of the site so that the robot can understand their content.
5. Check the correctness of symlinks so that when you go to other pages of the site, an infinitely growing URL is not created. For example, example.com/vasya/vasya/vasya/vasya/.
Look for more site structure recommendations from Yandex in help.
What is the right website structure?
Proper structure is important for both the user and search engines. Briefly about the main advantages of a properly organized structure:
1. Usability enhancement. Simple and convenient navigation allows the user to quickly find the information he needs. This will keep him on the site and improve behavioral ranking factors.
2. Speed up page indexing. The logical structure of a site helps crawlers understand which pages are important to the webmaster and end user. Optimizers adhere to the three-click rule, where the most important pages should not be more than 3 clicks from the main one. Otherwise, search engines may not index the page, do it later, or its priority will be very low.
3. Reducing the number of technical errors. The correct structure will avoid a large number of page duplicates, which will save time and money on promotion.
4. Distribution of internal link weight. Link equity is distributed according to the importance of the pages. It is necessary that a sufficient number of internal links lead to the promoted pages. The more links lead to priority pages, the more important they are for search engines.
5. Coverage of a large number of requests. Creating additional sections, categories and landing pages for narrow groups of queries makes it possible to rank for a large number of keywords. Such pages will be more relevant to a selected narrow group of queries, which will attract more organic traffic.
Types of site structures
To understand which structure to use, you need to understand the advantages and disadvantages of each. There are these types of structures:
Linear - the layout of pages in the form of a chain. The user gets to the main page, and all subsequent pages flip through like a book. There is no hierarchy in this structure and all pages are equal. They are viewed one after another, starting with the first and ending with the last. It is important that the pages have links to each other.

This structure is not very suitable for attracting users, since only the main page can be promoted. Link equity flows from the main page, passing it to all subsequent pages, and ending with the last page.
The linear structure is best used for business card sites, presentation sites, landing pages and others.
Linear structure with branches. The same principle as the linear one, only here there are branches within the chain.
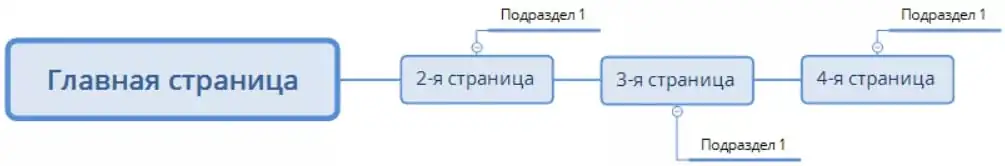
Such a structure, as a rule, is found in small corporate sites, author blogs, online books, landing pages, business card sites, and others.
Block (lattice) site structure. In this structure, all pages are equal, except for the main one. All blocks are located next to each other and link to several others. Link equity is evenly distributed. This arrangement of pages has a good effect on the indexing of the site.
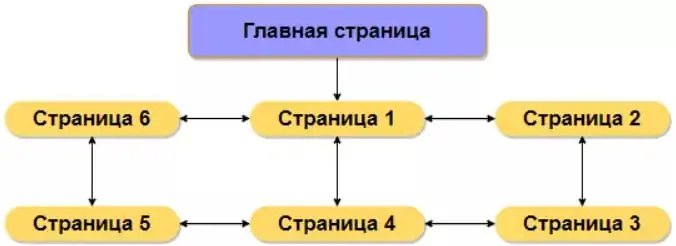
A block structure is usually used for a specific service or product, where each page describes a feature or type of service.
This scheme is not often seen, as it is not suitable for every site and is difficult to implement.
Tree-like (hierarchical) site structure. The most popular and optimal option for most sites. Each subsequent page is part of the previous one.
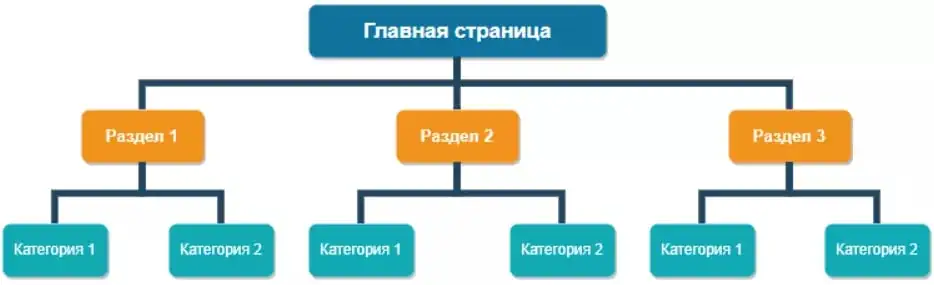
This is the best option for SEO, as the layered structure allows you to highlight more important pages for promotion.
The versatility of the tree structure allows it to be used for sites of different types. It is used for online stores, information resources, commercial sites, portals, and so on.
Errors when creating the site structure
It is important not to make mistakes when creating the site structure. They can create a lot of problems for the site owner. Let's look at the typical mistakes webmasters make:
The page is optimized for different intent (the meaning that the user puts into the query in the search engine). For example, using Serpstat, we check the frequency for the query "pedestals and chests of drawers". We see that users do not often enter such a phrase in the search:
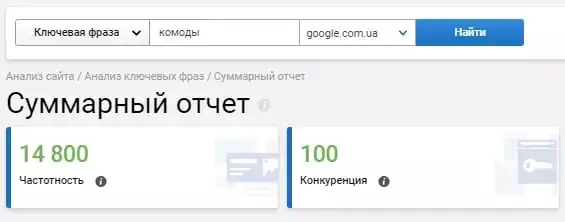
It will be much more efficient if you create a separate "Tables" page and a "Chest of drawers" page:

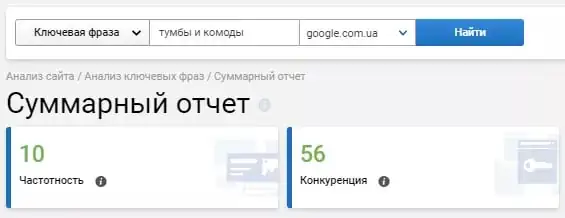
Thus, you will have two relevant pages on the site and the opportunity to get significantly more traffic.
What are internal page duplicates and how to deal with them
Duplicate pages. Let's take a fishing site as an example. The webmaster created the "Reels" section, which contains the "Backup reels" category:

Also created a filter "Type" with the value "Bulletinator Coil":
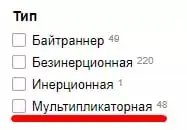
Thus, there are two identical pages on the site that begin to compete with each other in the search results for targeted queries. This leads to a deterioration in the ranking of the site, the loss of natural link mass and a change in the relevant page in the search results, since the search engine does not understand which page to show for a particular query.
Fuzzy duplicates. Another common mistake is the so-called “page cannibalization”. When specialists for similar groups of requests create different pages on the site.
For example, a flower delivery site has different pages: cheap flowers, cheap flowers, budget flowers.
Such pages lead to problems with site indexing. This must be taken care of at the stage of collecting the semantic core and clustering.
Pages with a large level of nesting. Web pages with the fourth and higher levels of nesting are often poorly indexed by search engines. The structure of the site must be thought out so that important pages are a maximum of three clicks from the main one. In cases with large sites and online stores, this cannot be avoided. For such projects, sitemaps are created and competent internal linking is set up to show priority pages to users and robots.
No sitemap. The error also affects the page indexing speed. For large projects, you need to create two sitemaps:
for search robots - the Sitemap.xml file, which is located in the root of the site. It shows the crawler all the pages needed for indexing and informs the crawler about the appearance of new pages;
for users - a separate page with a list of all the important pages of the site, arranged in a hierarchical order. The purpose of such a page is to simplify site navigation.
For small web resources, the lack of sitemaps is not a critical mistake.
Incorrect page distribution. It is important to create new pages on the site in such a way that they correspond to the semantic load of the previous pages. That is, they were correctly distributed into the relevant sections and categories. Refrigerators should be in the Large Appliances section, not the Plumbing section. But such solutions are not always obvious, for example, should air conditioners be in climate control equipment or in household appliances?
Remember
- The logical structure of the site is the basis of your web resource. The success of further interaction between users and search robots with the site depends on how correctly and efficiently the structure is worked out.
- When creating the correct structure of the site, it is necessary to follow the recommendations of search engines.
- Advantages of the logical structure:
- usability improvement;
- page indexing acceleration;
- reducing the number of technical errors;
- distribution of internal link weight;
- coverage of a large number of requests.
- The type of structure depends on the type of your site:
- linear structure of the site;
- linear with branches;
- block structure;
- tree structure.
- Typical mistakes when creating the correct structure:
- the page is optimized for different user intent;
- page duplicates;
- fuzzy doubles;
- high level of nesting of pages;
- lack of sitemaps;
- non-observance of the page hierarchy.
A source: Netpeak

