Long-tail SEO - how to promote for low-frequency queries and why you need it
Author - Constantin Nacul
1. What are long-tail queries?
1.1 Thematic long-tail queries
1.2 Complementary long-tail queries
1.3 Mixed long-tail queries
2. Why are LT queries relevant for search?
2.1 Voice search
2.2 Question form
3. Effectiveness and Benefits of Long-tail SEO
3.1 Low competition
3.2 High conversion rate
3.3 Promotion for general keywords of a specific topic
4. How to find long-tail queries?
4.1 Searching LT with Google Search Console
4.2 Use search suggestions
4.3 Search through Yandex.Wordstat
4.4 Searching with Serpstat
4.5 Searching with Ahrefs
5. How to move along the long tail
5.1 Promotion for thematic long-tail queries
5.2 Promotion for complementary long-tail queries
5.3 Promotion for mixed long-tail queries
What are long-tail queries?
Long-tail queries (LT) have a low frequency and clearly express the user's intentions.
Their length doesn't matter. Most low-frequency queries consist of three or more words, but exact queries of one or two words are also included in the "longtail" category.
The ratio of query frequency and conversion is clearly illustrated by the search demand curve:
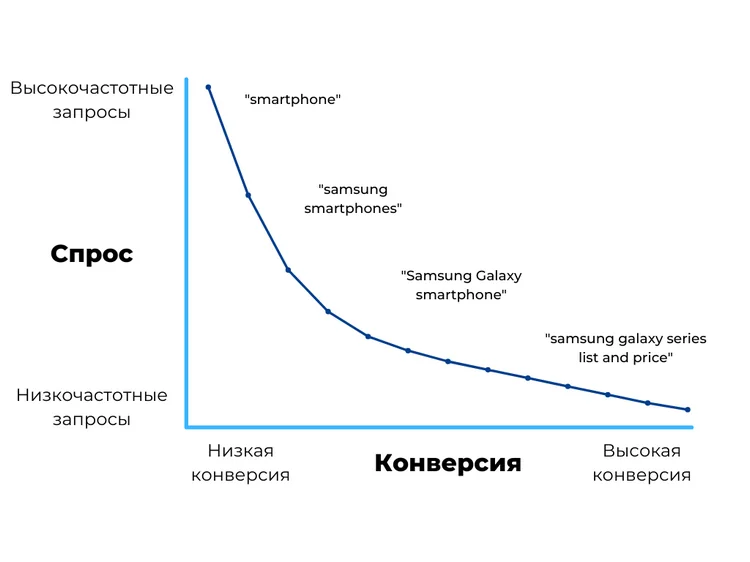
- in the world, a lot of users are interested in smartphones, entering a simple and high-frequency query "smartphone";
- it is possible to single out a narrower audience that is only interested in Samsung smartphones - the basic key of this category with a lower frequency of "samsung smartphones";
- further along the demand curve, requests are less and less frequent, for example, “Samsung Galaxy smartphone”;
- in the final part, experts consider a long list of requests, the frequency of which can range from one to five impressions per month or even be zero, for example, “samsung galaxy series list and price”.
The search demand curve shows that a huge number of keywords with low frequency add up to the so-called "long tail". The potential of which began to grow with the development of search engines and SEO in general.
There are three main categories of long tail queries:
- thematic;
- complementary;
- mixed.
Thematic long-tail queries
They point to a specific topic. The most accurate ones are suitable as the main keywords for pages that you want to promote for low-frequency queries.
For example, "how to learn to swim crawl." The query frequency is low: up to 540 impressions per month without specifying the region. In addition to special elements (blocks with advertising, videos, a list of local companies), the issue on it consists entirely of thematic materials that accurately answer the user's request.
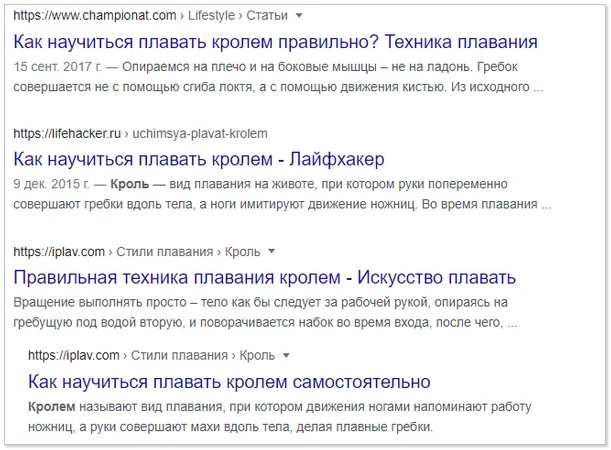
Thematic long-tail queries have the following characteristics:
- relatively complex wording;
- high detail;
- accurate intent.
The issuance of them is low competitive and consists of pages of a specific narrow topic. Using a competent promotion strategy, you can get to the top in thematic LT without much effort.
Complementing long-tail queries
They point to a specific topic, but because of their low frequency, they complement one or more broader topics.
Let's say the query is "sneaker lacing technique." Its frequency is up to 10 impressions per month. The issue will consist not only of pages about the methods of lacing sneakers, but also of pages about the technique of lacing shoes.
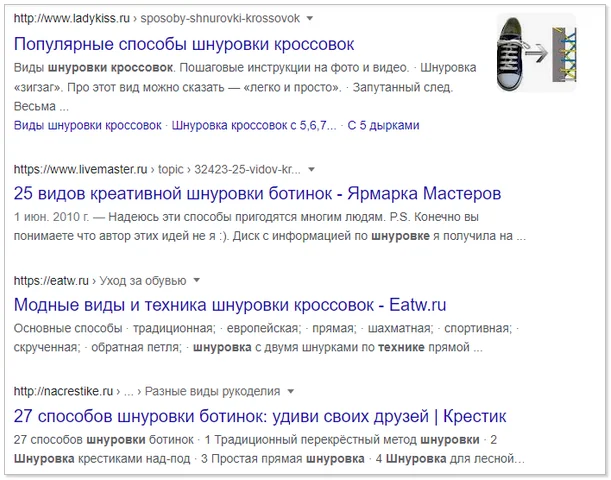
The frequency of the query "lacing shoes", also related to this topic, is higher - from 1600 impressions per month. This is the main feature of complementary LTs: increased competition due to the deduction in the issuance of results for common queries.
Using this type of long-tail in promotion is a more subtle tool. It is necessary to move in parallel on queries of high or medium frequency.
Mixed long-tail queries
They cannot be accurately assigned to any of the two previously given categories. Mixed LTs can refer to a specific narrow topic, but also cover several broader ones.
Examples of mixed long tail queries:
- Queries with pronounced seasonality are “seo trends 2022”.
- Names of organizations, specific places, cultural products (films, books, performances) - "science museum nemo".
- Low-frequency requests indicating the toponym - "where to buy a car in Odessa."
Due to the specifics of these keywords, search engines do not receive the necessary amount of data to provide experts with analytics on them in tools such as Google Ads. But there are some ways to parse long tail queries and even specific tools. I will tell about them further.
Why are LT queries relevant for search?
According to Google 15% search queries are new, users generate them every day. These statistics are based on low-frequency queries. Due to refinement or more complex intent formulation, users create new search terms. And they affect ranking algorithms.
Voice search
Part of the emergence of such a large number of low-frequency queries is due to the popularity of voice search. Accessories, voice assistants, products like Google Home have created a need for natural language search.
Search engines began to better understand the context of phrases, slang and adapt to the "conversational" style of queries. Conversational speech is developing dynamically, so the system algorithms are constantly being improved in order to correctly recognize queries in voice search.
Its popularization also works in the opposite direction: the constant generation of variations of the same query or phrase by users causes search engines to take them for the same. This happens to compensate for the increasing number of queries in the search.
Question Form
In addition to voice requests, people often use questions. Moreover, the same one can be asked in different ways (use introductory words that clarify details). And search algorithms learn to understand these LTs.
In this case, systems can take variations of the same request for the same. How to understand when this happens and why?
Perform N-gram analysis. An N-gram is a specific sequence of n elements. In the context of keywords:
the query "music" is a 1-gram;
the query "what kind of music can be used in tiktok" - 6-gram (sequence of 6 words).
Representing a query using an N-gram allows you to understand its naturalness, as well as the weight of each element n within the phrase.
Let’s say you want to optimize your content for low-frequency queries within the “exercise bikes” category. The query “which inexpensive exercise bike is better to buy” is best broken down using an n-gram. And to conduct an incomplete n-gram analysis - manually change each individual word in the phrase and see how and how much the search results change.
In some cases, you can use paid and free tools for n-gram analysis in SEO.
For example:
- !SEMTools;
- PEMAVOR;
- Ngram Analyzer.
Specifically, in the case of exercise bikes, replacing the words “inexpensive” with “budget”, “exercise bike” with “bike trainer” and even “buy” with “choose” will not play a significant role.
Issuance before changes:
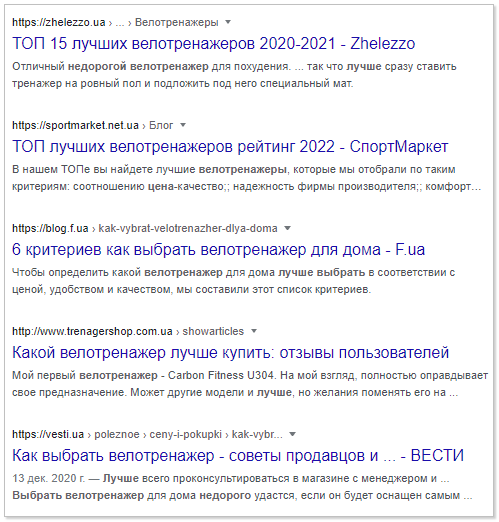
Output after changes:
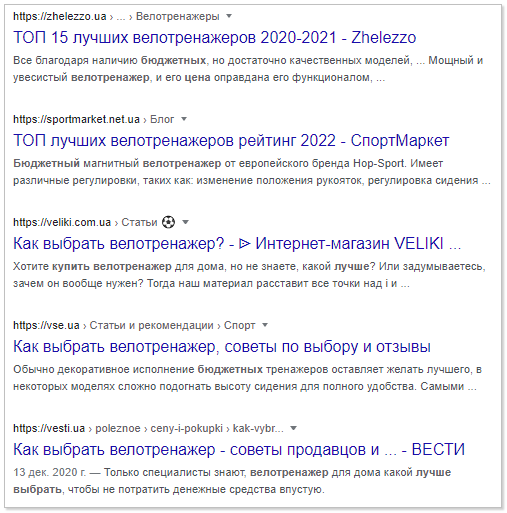
But a more noticeable change in search results will occur when the word “inexpensive” is replaced with “cheap”:
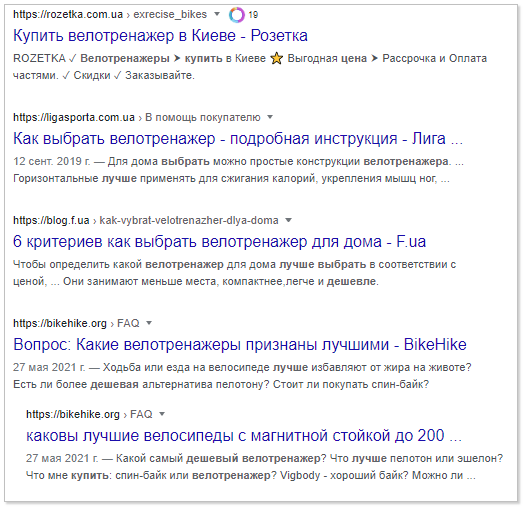
In any case, when analyzing the issue, it should be taken into account that the basis of the subject matter of the request depends on the word “exercise bike”, since it fully characterizes the intent.
Presenting queries with N-grams is not a panacea, and neither is tailoring for voice search. But they show that long-tails are relevant for search. The statistics and behavior of search engines are already signaling to SEOs that the use of low-frequency queries in promotion should be considered as a method with great potential.
The Effectiveness and Benefits of Long-tail SEO
In addition to being adaptable to voice search, long-tail keyword promotion offers at least three clear benefits.
Low competition
Most sites are promoted by high-frequency queries. In Ukraine, the query “buy iPhone 12” in Google gives 21.5 thousand results, and the query “buy iPhone 12 128 GB” - up to 100. A small number of competitors in search results can make it easier and faster to reach the top, but this is not means that there will be no competition at all.
Despite the low frequency, consumer demand can be medium to high. Therefore, when promoting for low-frequency keywords, check the changes in SERPs and the level of competition.
High conversion rate
This feature can be viewed from the angle of the sales funnel.
It includes:
- Awareness. At this stage, the user learns about a particular product and the possibility of acquiring it.
- Interest. The user has an interest in the product and the need to purchase.
- Wish. The need is formed, and the user wants to purchase the product.
- Action. A person buys a product to satisfy a need.
For example, when asking “buy a toothbrush”, the user is not yet at the stage of full awareness of his need, he does not know the types of toothbrushes and has not chosen a specific model. And with the request “buy an oral bi electric toothbrush”, the first two stages of the funnel are passed, the person knows exactly what he wants and is a few steps away from the purchase.
The specificity of low-frequency queries is that they are more targeted: the user can more specifically formulate his need, which means that he is more tuned in to the target action.
There are also additional advantages of promoting exactly on LT.
Promotion by general keywords of a specific topic
To reveal this feature, promotion by complementary long-tail queries is most suitable, since it implies the presence of the main thematic high-frequency queries. Search engines understand the topic of the query and can identify similar keywords that refer to the same intent. Therefore, the output result for LT may include some results for the main key as well.
But there is also a reverse process that should be taken into account: with proper optimization, low-frequency queries can raise the position of the site for the main high-frequency queries.
All three benefits of long-tail promotion can be represented through the principle of competitiveness:
- Top positions for high-frequency queries are not always attainable, especially in highly competitive niches with large promotion budgets.
- These difficulties prompt SEO specialists to abandon the simple, banal and ill-considered strategy of directly competing with sites in the top and pay attention to long-tail queries that are not very attractive at first glance.
- By choosing a more “subtle” promotion strategy in a highly competitive niche using low-frequency keywords, you can achieve more targeted traffic, and, as a result, more targeted actions.
How to find long-tail queries?
The main preparatory stage before moving on long-tail is to find them. This can be done in several ways.
Searching LT with Google Search Console
First of all, to search for low-frequency queries, unload the list from the "Efficiency" tab in Google Search Console. It contains the keywords that your site is already ranking for. And, as a rule, most of them are low-frequency.
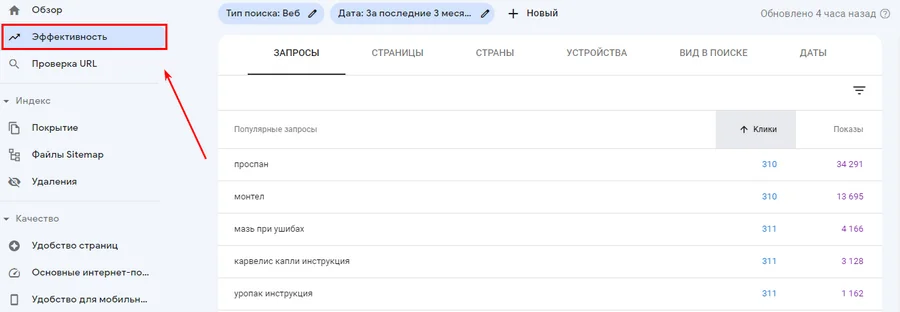
So you will find ready-made basic long-tail queries for which you do not have to create separate pages and a large amount of content. Search engines initially recognize them as suitable for pages on your site.
Use search suggestions
Search suggestions in Google and Yandex are almost the most effective way to find long-tail queries. Just start typing a phrase into the search bar. The system itself will add it in a pop-up window. Moreover, this process takes place according to the principle “the longer the phrase you enter, the less frequent the request you receive.”
Example on Google:
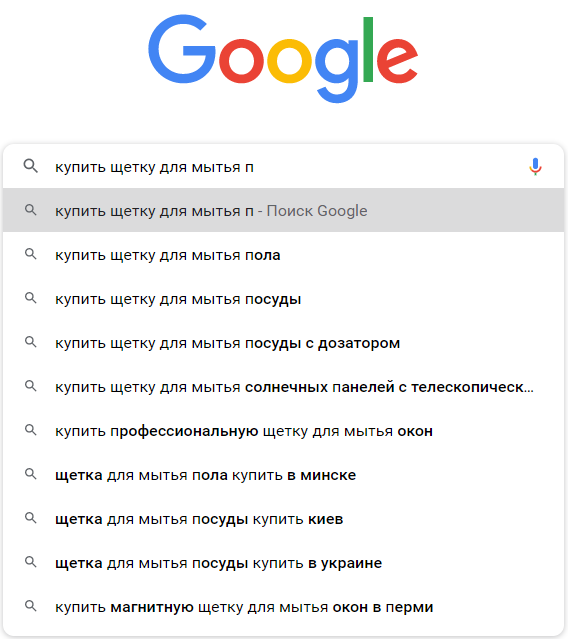
Example in Yandex:
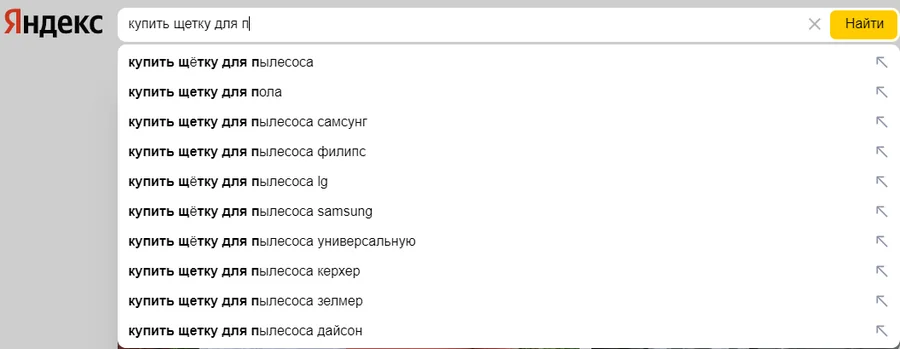
You should also pay attention to additional blocks with related queries on the SERP page, they can also contain useful low-frequency queries.
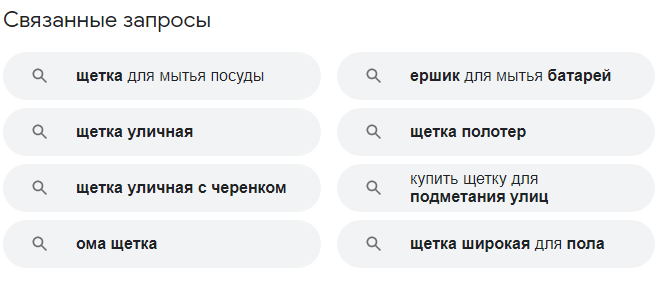

Never ignore this method when selecting a list of long-tail keywords, since all queries from search suggestions are real and natural for the user.
Search through Yandex.Wordstat
Yandex.Wordstat is a basic free tool for selecting keywords: both high-frequency and low-frequency ones.
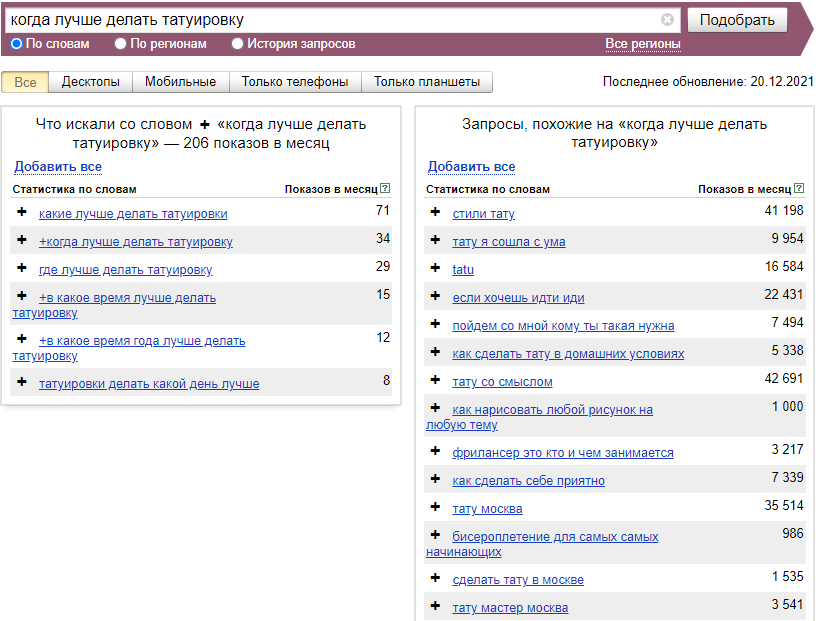
Through it, you can collect information semantics for any Russian-speaking region, since it is geo-independent.
Search via Serpstat
Serpstat is a paid tool with the richest set of functionality for selecting long-tail keywords.
The service allows you to search for key phrases and filter them by the level of required frequency.
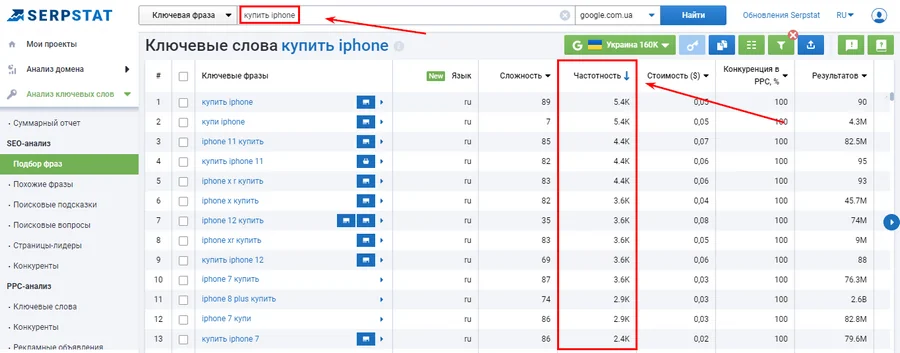
Additional sections of the tool will help you search for long-tail queries:
- "Similar Phrases" Allows you to find similar and complementary low-frequency queries and expand the list;
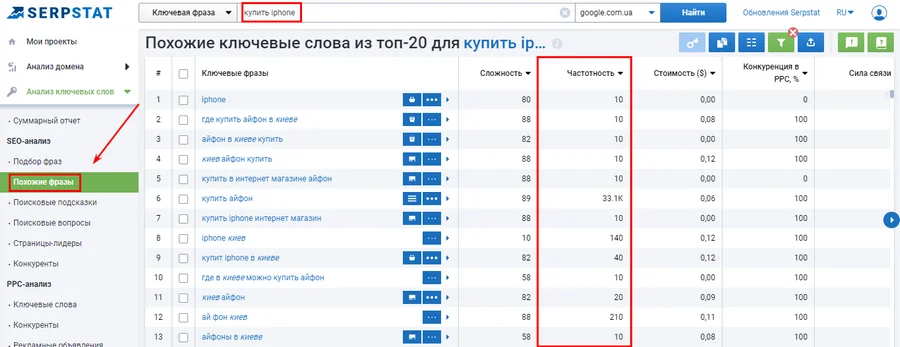
- "Search Tips" Does not contain statistical data on requests, but is suitable for quick selection of native long-tail keywords - the most natural for everyday human speech;
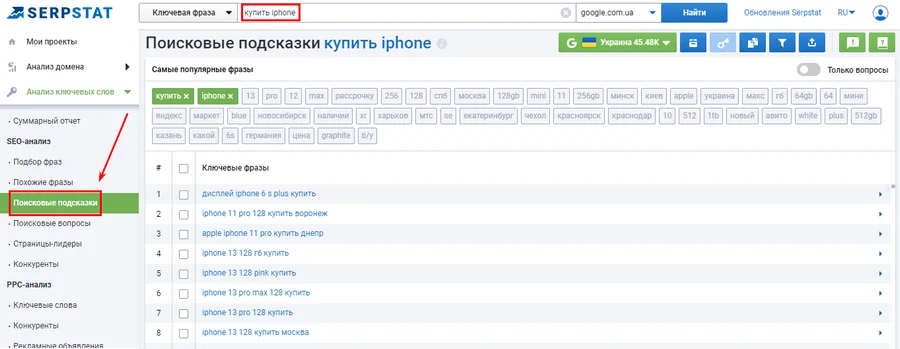
- through the "Search questions" you can easily collect information topics on a specific topic. It is most suitable for forming the FAQ block on commercial pages and for creating the basis for the site's blog materials.
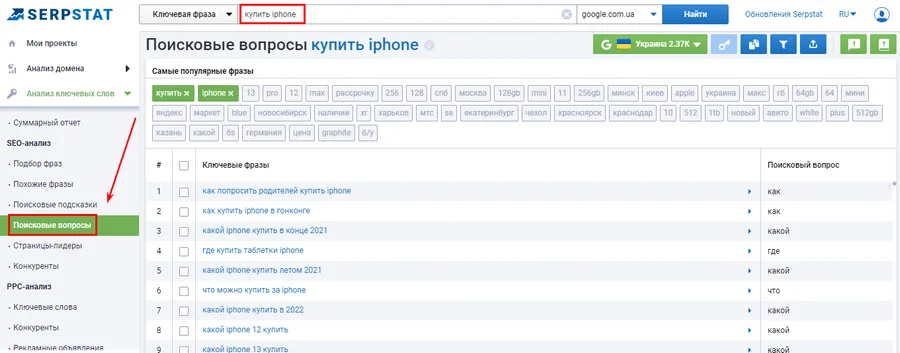
Search with Ahrefs
The second paid tool on our list. The functionality is similar to Serpstat: it is possible to select requests and filter them by the maximum and minimum frequency. And the Questions report will show search questions on the desired topic.
The service has several very convenient features:
- Displaying several categories of keywords at once for your query. In a special Keyword ideas block, you will see information on keywords, search queries, complementary long-tail and similar phrases.
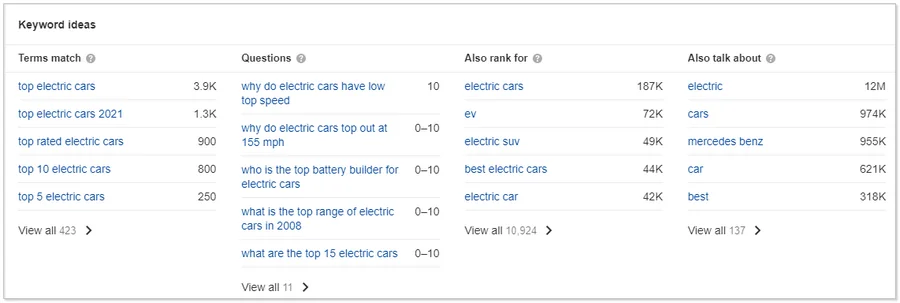
- Displaying the top pages for a specific query with detailed information about the link profile and the main keyword.
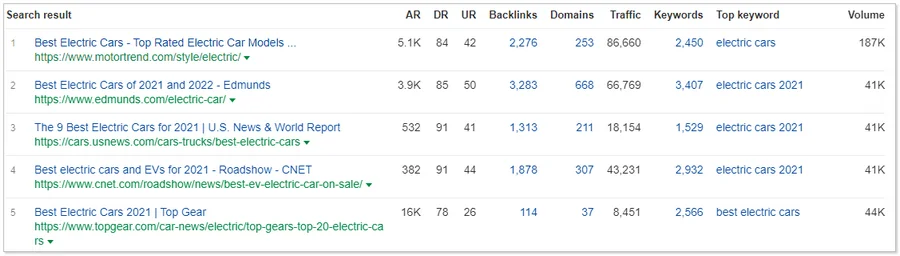
- Show top pages of similar topics.
The tool stands out as a good base for the English-language search segment. If you are moving under America, Europe or other regions, be sure to check it out.
There are a large number of third-party sites for matching low-frequency queries with free or trial versions. For example, AnswerThePublic, which can show a whole cluster of search questions for the main query.
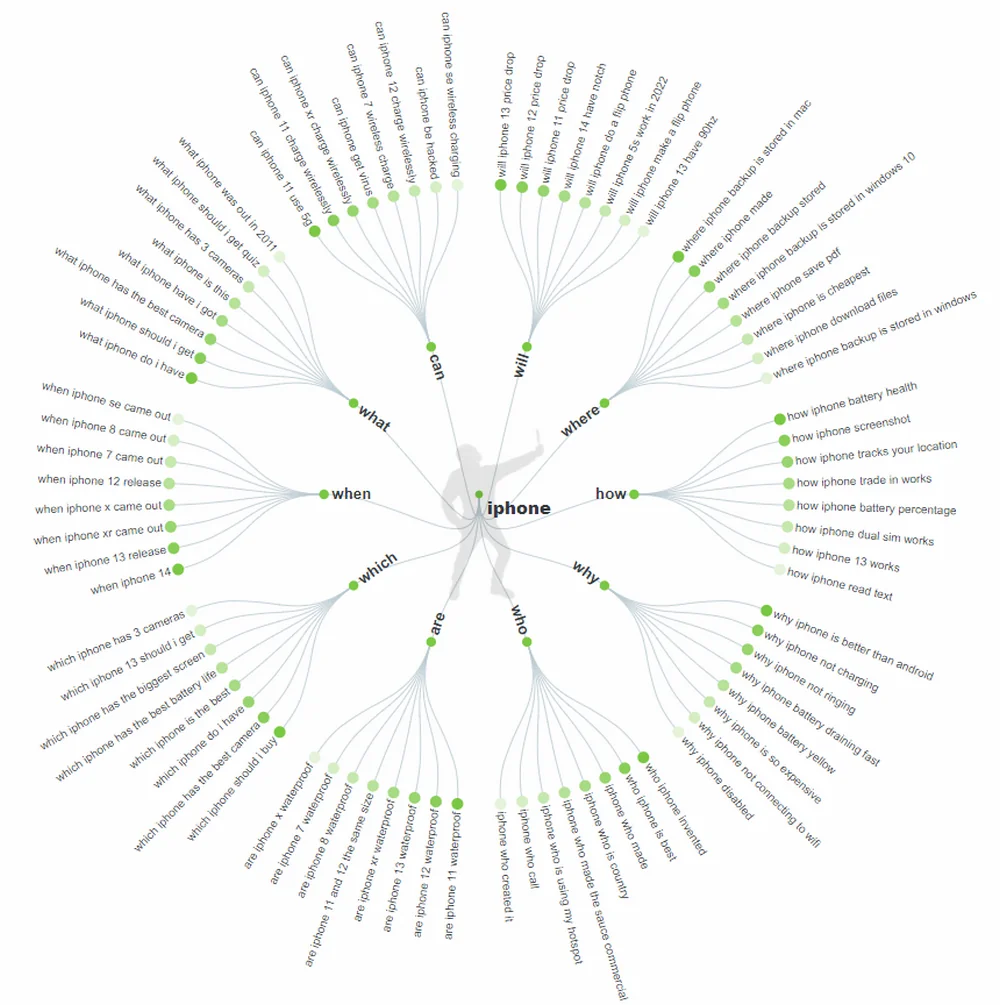
Use all possible ways to select long-tail queries, explore the search results for them, cluster the lists and filter out the unnecessary, in order to ultimately compile a list of the most suitable keywords for promotion.
How to advance along the long tail
After collecting suitable requests, it is necessary to decide on the right promotion strategy. To do this, it is important to know how the search engine generates results and how it understands the intent of the request.
Let me remind you that there are three types of LT queries. And each of them characterizes the intentions of the search engine.
| Request type | Search engine actions |
| Thematic LT queries | The system includes only targeting thematic pages in the results for a specific query. |
| Complementary LT Queries | Includes search results for more frequent queries. |
| Mixed LT Queries | Makes output mixed. |
Promotion by thematic long-tail queries
The search results for thematic LTs consist entirely of thematic materials that accurately answer the user's query.
Here is the output for the query "how to find low-frequency queries."
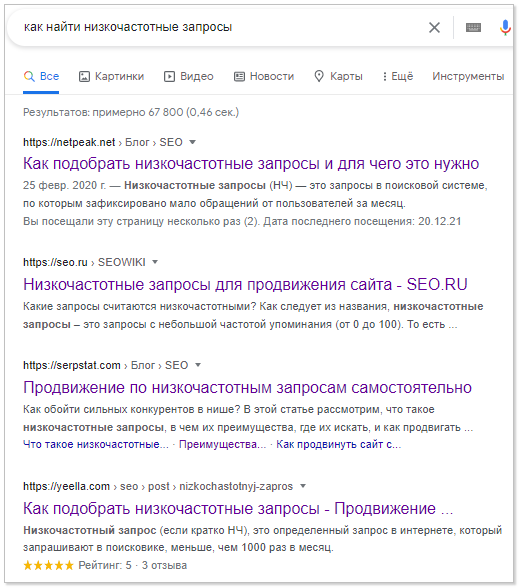
It consists only of materials suitable for a specific request. Therefore, the most successful would be to create a separate page and promote it under thematic LT or a semantic group of queries.
The semantic group may consist of variants of the key phrase:
- “how to find low-frequency queries”;
- “how to collect low-frequency queries”;
- "how to pick up low-frequency requests".
The output for each request will look almost the same, but there will still be changes. This gives you the choice of how to progress depending on your budget and time. You can create the most targeted page for each element from the group and promote it separately. Or create a common page with a larger-scale material and promote it for several keyword options at once.
You can go further and collect even less frequent queries using geotags, comparing some terms with others, complicating the question form, and so on. You can create a separate section on the site for a specific topic and include pages with questions and exact answers, each of which will be promoted for a specific request.
The main thing in this promotion scheme is that the issue does not contain a large number of competitor pages that contain large-scale materials promoted by high-frequency queries.
Using this strategy, you will collect more traffic by ranking in the top for each low-frequency request. And this is easier to do than to promote one or two high-frequency queries to the top in a competitive niche. Each of the pages may collect a small amount of traffic, but in combination they will provide a considerable amount. Moreover, traffic on low-frequency queries will be more targeted.
Promotion for complementary long-tail queries
Complementary LT results are formed with a large number of pages promoted by high-frequency queries. By choosing this type of promotion, you should not create separate pages for each request. Spend a lot of effort and budget, and search engines will consider them part of another, larger topic.
Therefore, complementary keywords should be used in promotion auxiliaryly. Analyzing the top results for them, you will find the main queries in the subject: they can be both thematic long-tail and medium- or high-frequency queries.
In this case, in your promotion strategy, rely on the main queries, and for complementary long-tail phrases, create additional paragraphs or blocks of information, for example, the FAQ block.
If you can reach the top with such a page for the main query, most of the LTs that complement it will also reach the top. This way you will get more traffic for complementary long-tail queries.
Promotion for mixed long-tail queries
Mixed LT results include both pages with the exact satisfaction of the user's intent, as well as pages that relate to related broad topics.
The promotion strategy for keywords with this ranking feature is flexible. You can promote requests as complementary, or vice versa - as thematic ones.
In the first case, it is necessary to create large materials that will include many low-frequency queries and blocks with additional information, as well as significantly increase the degree of page authority for search engines by pumping up the link profile.
In the second case, you need a narrowly focused material or several materials for individual requests with a full disclosure of the topic, and it is also important to link them to each other and to other materials on the site using internal links.
The choice of strategy depends on the availability of time, budget and your skills. But one thing is clear - high-quality and unique content that is useful to users is one of the most important factors when promoting long-tail queries.
Study the top keywords and make a list of the content that needs to be mentioned on the page and the features that make the page a quality one. We are talking about technical optimization (say, download speed) or about the requirements of the search engine for content. This list will serve as a basis for building quality content around long-tail queries.
Remember
LT is a type of low-frequency queries that clearly express the user's intent. With the development of voice search in particular and the field of SEO in general, they are becoming more and more interesting for promotion. They have low competition, a high conversion rate, and it is possible to immediately get into the search results for similar high-frequency keywords.
Before advancing through LT, you need to find them. There are a number of tools to help you do this:
- Google Search Console
- search suggestions in Google and Yandex;
- Yandex.Wordstat;
- Serpstat;
- Ahrefs;
- sites for the selection of low-frequency queries, for example, AnswerThePublic,
There are three types of long-tail queries:
- thematic - indicate a specific topic, the issue on them consists of landing pages;
- complementary - complement one or more broader topics; due to low frequency, they will get into the search results
- related pages;
- mixed - relate to both a narrow topic and cover a broader one, the output will be mixed.
Each of these types has its own promotion scenarios.
Long-tail seo is a fairly flexible tool that, in the right hands, can bring a huge amount of targeted traffic to the site. But you should not focus on low-frequency keywords and focus on creating 100 or 200 highly targeted pages filled with template content.
Properly implement long-tail keywords in the semantic space of your project, work on the quality of content, analyze the niche of your site and monitor the global reaction of search engines to LT keywords. All this is the key to success in promoting the site according to the long-tail principle.
A source: Netpeak

